import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltEuler’s Method
Euler’s method is a simple numerical technique used to approximate the solutions of ordinary differential equations (ODEs). It works by iteratively calculating the values of a function at discrete time steps.
Import Libraries
Exact Equation
Define the Equation
\[\large v = \frac{m \cdot g}{c} \cdot \left( 1 - e^{\large -\frac{ \large c \cdot t}{\large m}}\right) \]
def eqn(t, m, g, c):
v = (m*g/c)*(1-np.exp(-c*t/m))
return vGenerate x values
x = np.linspace(0, 40, 400)Constants
m=80 #(Mass = 80 Kg)
g=9.81 #(Gravitational Const. = 9.81 m/s^2)
c=12.5 #(Drag Coeff. = 12.5 Kg/s)
v_0=0 #(Given that at t=0, v=0)Calculate y values
y = eqn(x, m, g, c)Plotting the Exact Function
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('v')
plt.title('Plot of Exact Equation')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()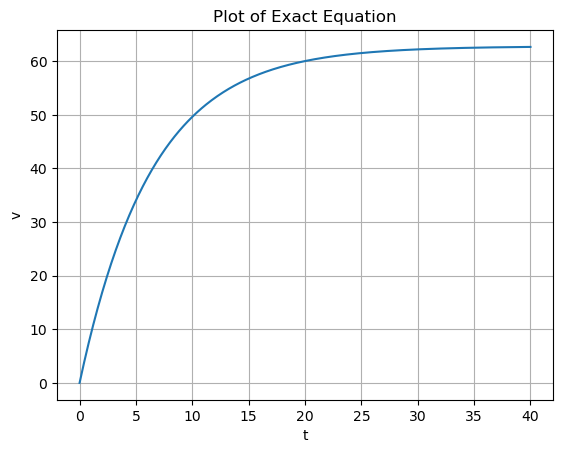
Euler’s Method
\[ \large f(t + h) = f(t) + h \cdot f'(t) \]
Define Differential Eqn
def differential_eqn(v,t):
return g-c*v/mGenerate x values with step size
step=1
x_e = np.linspace(0, 40, int(40/step))Calculate y values
y_e=np.zeros(len(x_e))
y_e[0]=v_0
for i in range(len(x_e)-1):
y_e[i+1]=y_e[i]+differential_eqn(y_e[i],x_e)*stepPlotting the Estimated Function
plt.plot(x_e, y_e)
plt.xlabel('t')
plt.ylabel('v')
plt.title('Plot of Estimated Equation')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()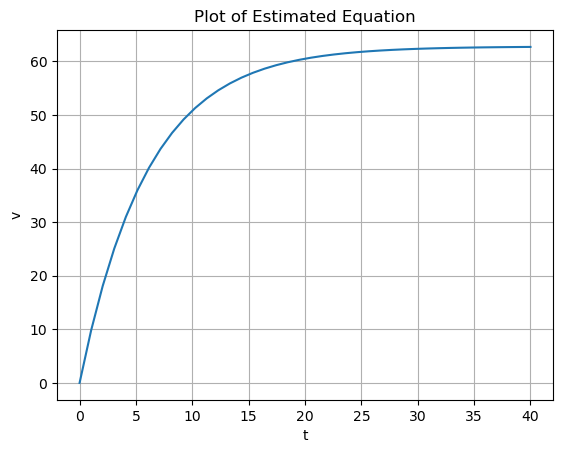
Calculating the error
plt.plot(x_e, y_e, label="Solving by Euler's Eqn")
plt.plot(x, y, label="Solving by Exact Eqn")
plt.title('Plot of Exact and Estimated Equation')
plt.legend()
plt.show()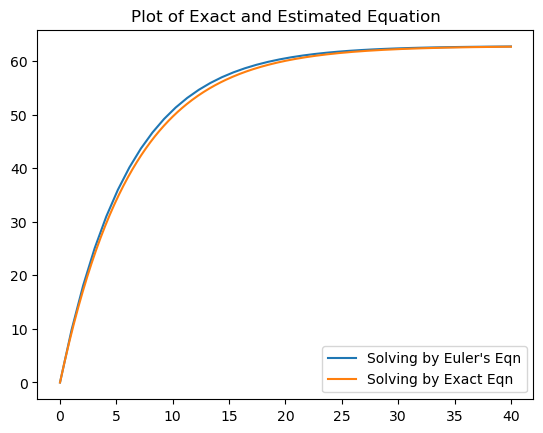
y1=y[::10]+1e-15
absolute_error = np.abs(y1 - y_e)
percentage_error = (absolute_error / y1) * 100
average_percentage_error = np.mean(percentage_error)
print("Average Percentage Error:", average_percentage_error, "%")Average Percentage Error: 4.475024083304925 %